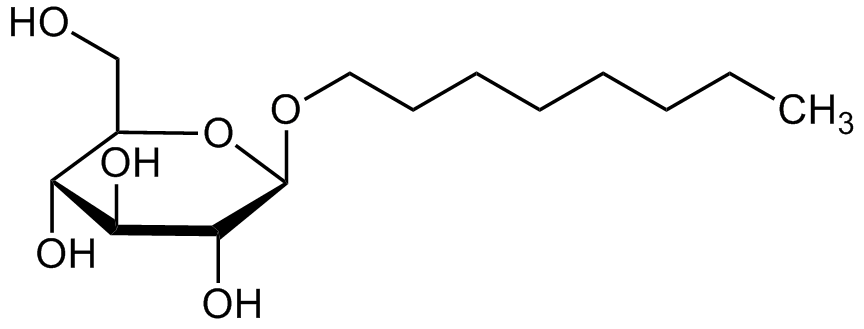
n-Octyl-beta-D-glucopyranoside (ultrapure)
Product Code:
AG-CC1-0008
AG-CC1-0008
Antibody Isotype:
n/a
n/a
Antibody Clone:
n/a
n/a
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Ambient
Storage:
-20°C
-20°C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CC1-0008-G001 | 1 g | £45.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CC1-0008-G005 | 5 g | £150.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CC1-0008-G025 | 25 g | £500.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: Switzerland.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Show All
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
OG; n-Octylglucoside; n-Octyl-beta-D-glucoside; BTB11967
Appearance:
White powder.
CAS:
29836-26-8
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Handling Advice:
Hygroscopic.Protect from light and moisture.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C14H28O6/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-19-14-13(18)12(17)11(16)10(9-15)20-14/h10-18H,2-9H2,1H3
InChiKey:
HEGSGKPQLMEBJL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 29836-26-8. Formula: C14H28O6. MW: 292.4. Non-ionic detergent for the functional solubilization, isolation, purification and crystallograpy of membrane proteins. Mild, non-denaturing detergent that is used for the solubilization and reconstitution of membrane-bound proteins in their native state and for the preparation of lipid vesicles. Its well-defined chemical structure, small uniform micelles and high water solubility make it superior to most other non-ionic detergents for membrane solubilization. The high critical micelle concentration (0.7%) of n-octylglucoside facilitates ready removal from final protein extracts by dialysis or gel filtration. Used in lysis and solubilisation buffers for bacterial lipoprotein preparations, mitochondrial extracts or for determination of protein content by BCA assay. Can be used in 2D electrophoresis and to improve selectivity of immunoprecipitation of phosphotyrosine modified proteins and to increase the resolution of proteins in 2D gels.
MDL:
MFCD00063288
Molecular Formula:
C14H28O6
Molecular Weight:
292.4
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
Non-ionic detergent for the functional solubilization, isolation, purification and crystallograpy of membrane proteins. Mild, non-denaturing detergent that is used for the solubilization and reconstitution of membrane-bound proteins in their native state and for the preparation of lipid vesicles. Its well-defined chemical structure, small uniform micelles and high water solubility make it superior to most other non-ionic detergents for membrane solubilization. The high critical micelle concentration (0.7%) of n-octylglucoside facilitates ready removal from final protein extracts by dialysis or gel filtration. Used in lysis and solubilisation buffers for bacterial lipoprotein preparations, mitochondrial extracts or for determination of protein content by BCA assay. Can be used in 2D electrophoresis and to improve selectivity of immunoprecipitation of phosphotyrosine modified proteins and to increase the resolution of proteins in 2D gels.
Purity:
>99% (HPLC) | [alpha-Isomer <2% (NMR)] | [n-Octanol: <0.005%]
SMILES:
OCC1[C@@H](O)C(O)[C@H](O)[C@H](OCCCCCCCC)O1
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in water (100 mg/ml), DMSO or DMF.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 3 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
Documents
References
Effects of octyl beta-glucoside on insulin binding to solubilized membrane receptors: R.J. Gould, et al.; Biochemistry 20, 6776 (1981) | Reconstitution of Membrane Receptor Systems: A. Levitzki; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 822, 127 (1985) | Micellar Properties of Octylglucoside in Aqueous Solutions: K. Kameyama, et al.; J. Colloid Interface Sci. 137, 1 (1990) | Reconstitution of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase: mechanisms of membrane protein insertion into liposomes during reconstitution procedures involving the use of detergents: D. Levy, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1107, 283 (1992) | Molecular dynamics characterization of n-octyl-beta-D-glucopyranoside micelle structure in aqueous solution: P. Konidala, et al.; J. Mol. Graph. Model 25, 77 (2006) | Use of detergents to increase selectivity of immunoprecipitation of tyrosine phosphorylated peptides prior to identification by MALDI quadrupole-TOF MS: G. Zhan & T.A. Neubert; Proteomics 6, 571 (2006) | Development and crystallization of a minimal thermostabilised G protein-coupled receptor: T. Warne, et al.; Protein Expr. Purif. 65, 204 (2009) | Mass spectrometry of intact membrane protein complexes: A. Laganowsky, et al.; Nat. Protocols 8, 639 (2013) | Low-Resolution Structure of Detergent-Solubilized Membrane Proteins from Small-Angle Scattering Data: A. Koutsioubas; Biophys. J. 113, 2373 (2017)